Stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, either due to a blocked artery or a burst blood vessel. It can lead to severe complications, including paralysis, speech difficulties, and cognitive impairment. Many strokes are linked to hidden risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, stress, and unhealthy lifestyle habits. Understanding and addressing these silent contributors is key to prevention and early intervention.
What causes a stroke?
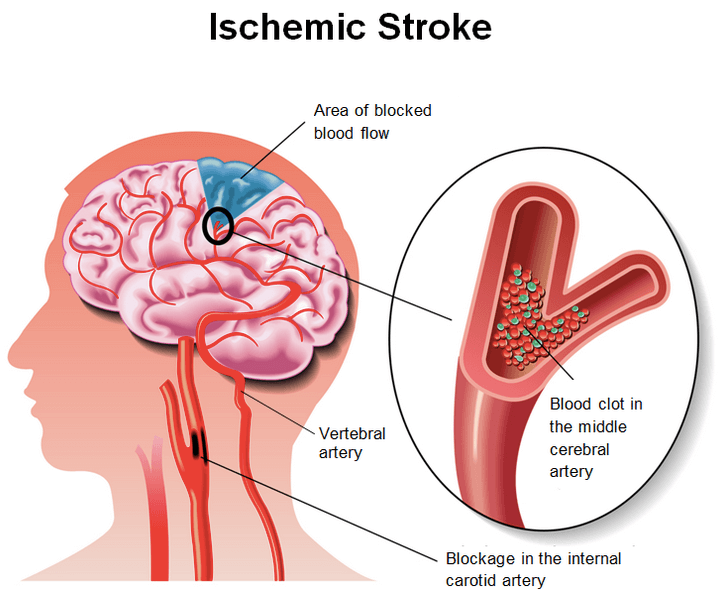
Lack of blood supply to the brain. When blood flow to the brain stops, the brain cells are deprived of oxygen and begin to die. This can happen when a blood vessel bursts or leaks and no longer can deliver the blood supply to a part of the brain.
Symptoms and causes of stroke
A stroke happens when blood flow to the brain is blocked or a blood vessel bursts. Symptoms depend on which part of the brain is affected. Common signs include:
- Trouble speaking or understanding (aphasia)
- Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body or face
- Loss of coordination or clumsiness (ataxia)
- Sudden confusion or memory problems
- Severe headache
- Dizziness or loss of balance
- Vision problems (blurry or double vision)
- Nausea or vomiting
What Causes Strokes?
There are two main types of strokes:
1. Ischemic stroke: caused by a blood clot blocking blood flow to the brain. Common reasons include hardened arteries (atherosclerosis), heart problems like atrial fibrillation, clotting disorders, and small vessel disease.
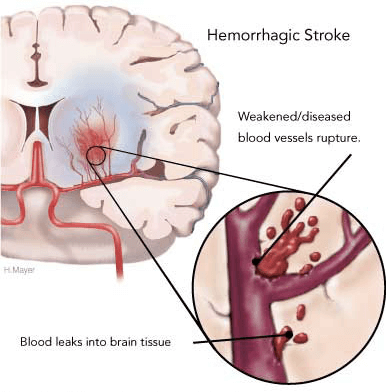
2. Hemorrhagic stroke: caused by a blood vessel in the brain bursting. This can happen due to high blood pressure, brain aneurysms, tumors, or conditions that weaken blood vessels.
Mini-stroke (TIA): A transient ischemic attack is like a stroke, but temporary. It is a serious warning sign and needs urgent medical attention.
What is the Treatment for a Stroke?
Treatment depends on the type of stroke.
Ischemic stroke: Doctors try to restore blood flow to the brain. This can be done with medicines like aspirin or emergency procedures to remove the clot. Quick treatment improves survival and reduces complications.
Hemorrhagic stroke: Doctors work to stop the bleeding and lower pressure in the brain. If the patient takes blood thinners, they may receive medication or a blood transfusion. Sometimes surgery is needed to fix damaged blood vessels.
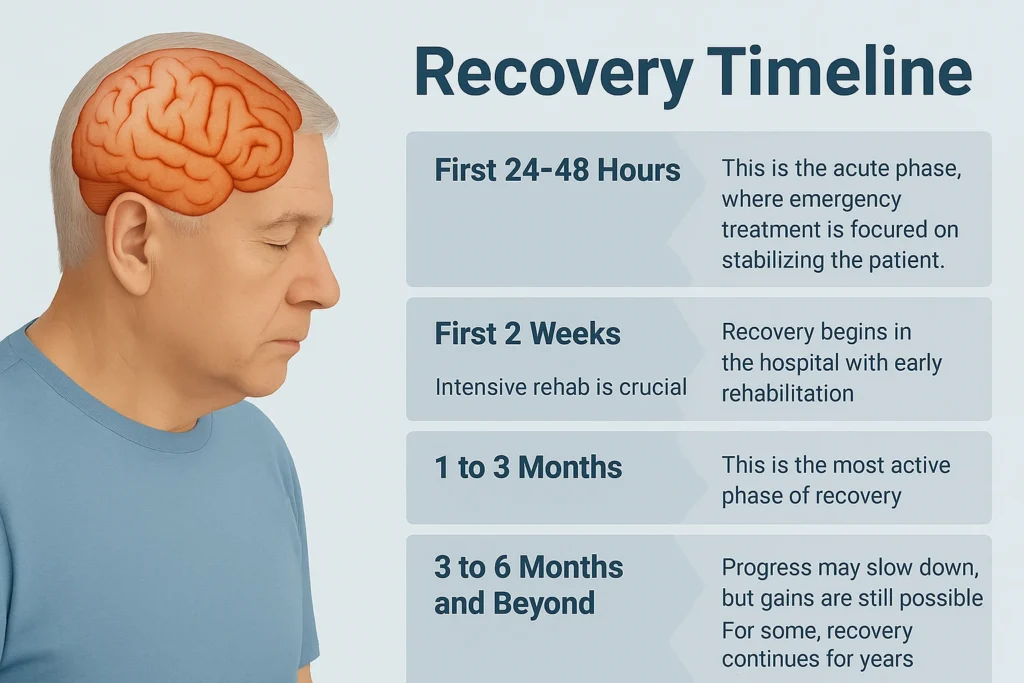
How Do I Take Care of Myself After a Stroke?
Recovering after a stroke takes time and effort. Once you and your doctor finalize your treatment plan, try to follow it as closely as possible. Here are some important steps:
- Attend your rehab and therapy sessions. Let your therapists know if anything feels unsafe or causes discomfort. Rehab can be challenging, but you shouldn’t be in constant pain.
- Pay attention to your mental health. Depression and anxiety are common after a stroke. Feeling sad or upset doesn’t mean you are weak. Emotional health is just as important as physical recovery. Talk to your doctor or a mental health professional if you need support.
- Take your medications as prescribed. Following your medication plan helps your body heal and supports recovery.





Leave a Reply